Enable Web Credential Sharing in Your Android App
This guide explains how to implement the W3C Digital Credentials API into the Multipaz Getting Started Sample app using the Multipaz SDK. The integration enables your app to present credentials to web-based verifiers using the standardized Credential Manager interface, including privileged browser and user agent support.
How It Works
When a user visits a web verifier (like verifier.multipaz.org), here's what happens:
On Device Verification (the verifier opened on the mobile device)
- Browser Request: The verifier website uses the W3C Digital Credentials API to request credentials
- Android Response: Your app (as a credential provider) receives the request and shows the credential selection UI
- Server Verification: The verifier server processes and verifies the returned credentials
- Result Display: The browser displays the verified credential information
Cross Device Verification (the verifier opened from another device)
- Browser Request: The verifier website shows an alert dialog with a QR Code
- QR Scanning: Scan this QR code form the device with a credential provider - say, a wallet app
- Android Response: Your app (as a credential provider) receives the request via redirection and shows the credential selection UI
- Communication: The app communicates with the server with the response to requested credentials
- Server Verification: The verifier server processes and verifies the returned credentials
- Result Display: The browser displays the verified credential information
The verifier server handles the complex cryptographic verification, while your Android app focuses on secure credential presentation.
Overview
The W3C DC API integration allows your app to interact with web-based verifiers via the Credential Manager API, supporting secure and privacy-preserving credential presentment flows. With this, users can share credentials directly with browsers that support the API. To implement this using Multipaz SDK, these steps are required:
- Implementing a new
CredmanActivityto handle credential requests. - Registering privileged user agents (browsers) via a
privilegedUserAgents.jsonfile. - Updating the app initialization to support exporting credentials through the API.
Implementation Steps
1. Dependencies
We would need to add the Multipaz DC API library for the Digital Credentials implementation.
gradle/libs.versions.toml
[versions]
multipaz = "0.96.0" # latest version of Multipaz Extras
[libraries]
multipaz-dcapi = { group = "org.multipaz", name = "multipaz-dcapi", version.ref = "multipaz" }
Refer to this code for the complete example.
composeApp/build.gradle.kts
kotlin {
sourceSets {
commonMain.dependencies {
// ...
implementation(libs.multipaz.vision)
}
}
}
Refer to this code for the complete example.
2. Add CredmanActivity
Create a new activity extending CredentialManagerPresentmentActivity provided by Multipaz. This activity is launched when a browser requests credentials via the W3C DC API.
// kotlin/CredmanActivity.kt
class CredmanActivity : CredentialManagerPresentmentActivity() {
override suspend fun getSettings(): Settings {
val app = App.getInstance()
app.init()
return Settings(
appName = app.appName,
appIcon = app.appIcon,
promptModel = App.promptModel,
applicationTheme = @Composable { content -> MaterialTheme { content() } },
documentTypeRepository = app.documentTypeRepository,
presentmentSource = app.presentmentSource,
privilegedAllowList = Res.readBytes("files/privilegedUserAgents.json").decodeToString(),
imageLoader = ImageLoader.Builder(applicationContext)
.components { /* network loader omitted */ }.build(),
)
}
}
Refer to the CredmanActivity file for the complete example.
3. Update AndroidManifest.xml
Register CredmanActivity in your manifest and declare intent filters for the Credential Manager API actions.
<activity
android:name=".CredmanActivity"
android:configChanges="orientation|screenSize|screenLayout|keyboardHidden|mnc|colorMode|density|fontScale|fontWeightAdjustment|keyboard|layoutDirection|locale|mcc|navigation|smallestScreenSize|touchscreen|uiMode"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="singleInstance"
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Translucent">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.credentials.registry.provider.action.GET_CREDENTIAL" />
<action android:name="androidx.identitycredentials.action.GET_CREDENTIALS" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
What does this do?
- This registers your app as a credential provider for browser and web app requests using the W3C DC API.
Refer to the sample Manifest code for context.
4. Add Privileged User Agents JSON
This JSON defines the trusted browsers (by package name and certificate fingerprint) that are allowed to handle credential requests, ensuring only verified apps can participate.
Create a JSON file listing all trusted browser apps and their signature fingerprints.
{
"apps": [
{
"type": "android",
"info": {
"package_name": "com.android.chrome",
"signatures": [
{
"build": "release",
"cert_fingerprint_sha256": "F0:FD:6C:5B:41:0F:25:CB:25:C3:B5:33:46:C8:97:2F:AE:30:F8:EE:74:11:DF:91:04:80:AD:6B:2D:60:DB:83"
}
// ... more signatures
]
}
}
// ... many more browsers
]
}
What does this do?
- Defines which browsers and apps can be trusted when requesting credentials from your app.
- Warns about untrusted applications/websites when they try to access sensitive credential data.
Refer to the full privilegedUserAgents.json file for a complete list.
5. Export Digital Credentials
Modify your app’s initialization to start exporting credentials if Digital Credentials are available.
class App {
// ...
suspend fun init() {
if (!isAppInitialized) {
// ...
if (DigitalCredentials.Default.available) {
DigitalCredentials.Default.startExportingCredentials(
documentStore = documentStore,
documentTypeRepository = documentTypeRepository
)
}
// ...
isAppInitialized = true
}
}
}
What does this do?
- Enables credential export functionality for the W3C DC API.
- Ensures the app is ready to respond to browser credential requests.
Refer to this code from App.kt for context.
6. Updating Reader Trust Manager
Make sure that you have configured the app's reader trust manager to trust the official Multipaz web verifier verifier.multipaz.org for sharing credentials.
- Note: Refer to the Reader Trust section for more details on this step
7. Testing and Verification
Test with Supported Browsers
- Install Chrome (or other listed browsers) on your Android device.
- Open verifier.multipaz.org
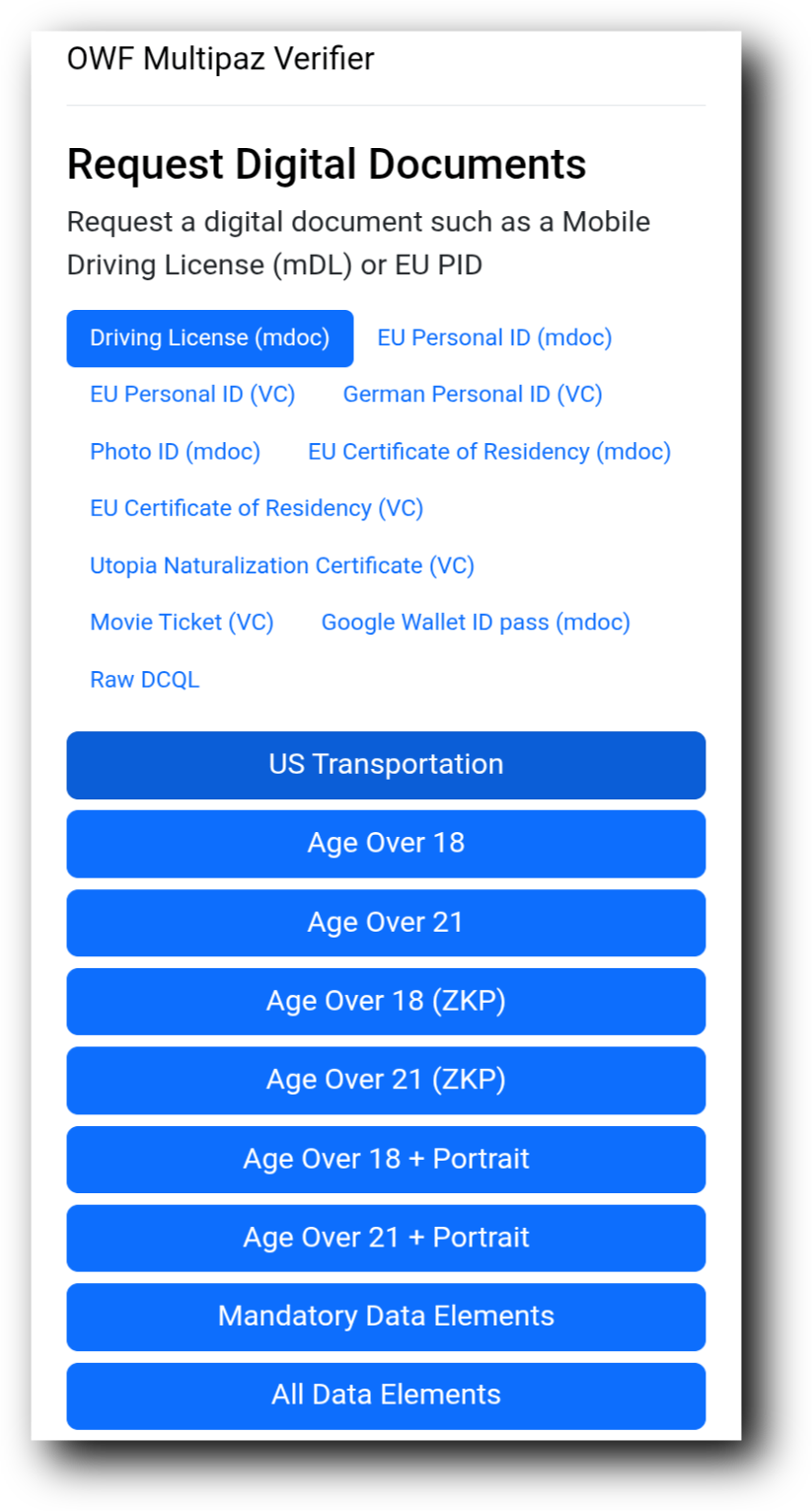
- Select “US Transportation” under “Driving License (mDoC)”
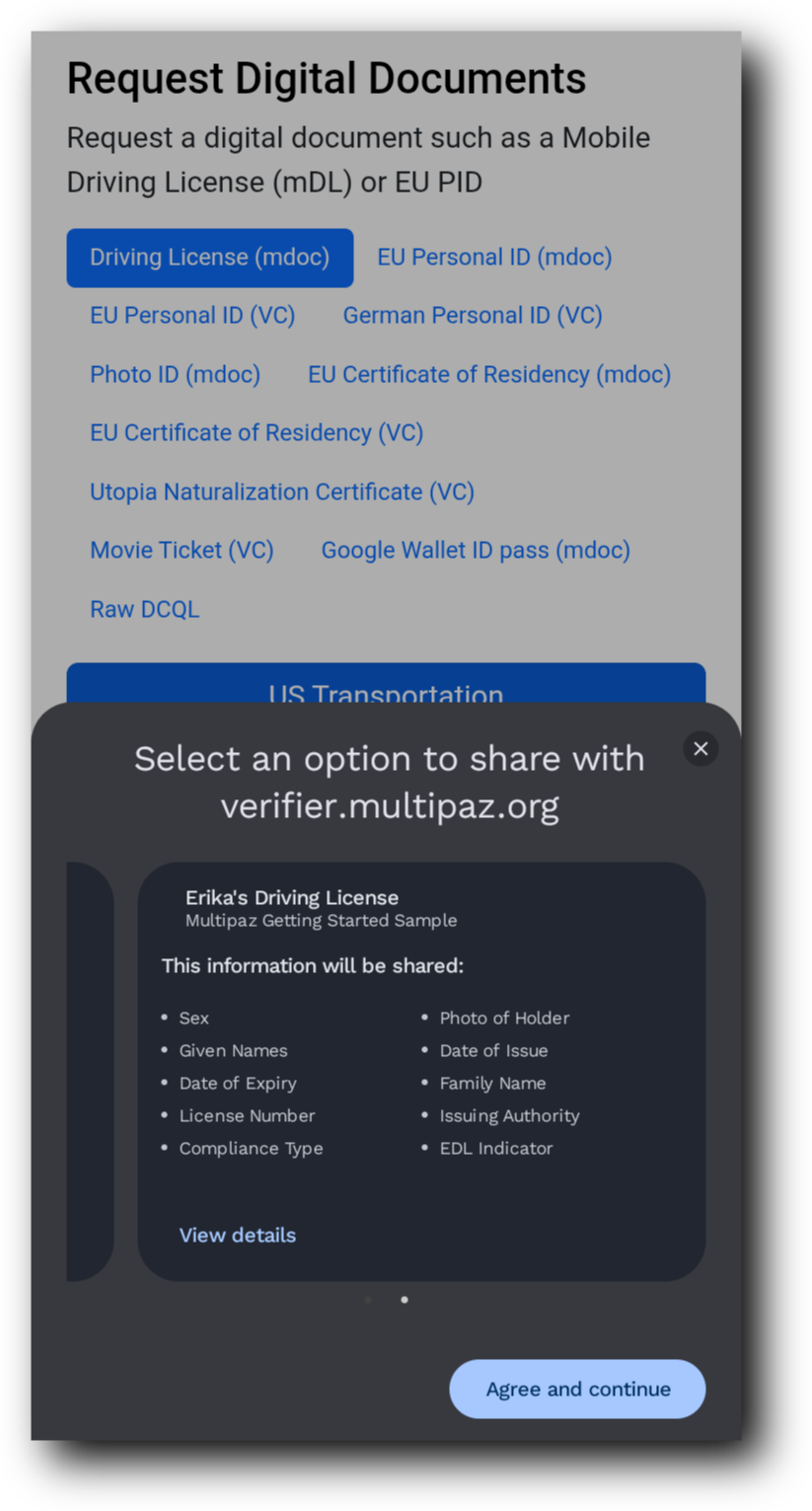
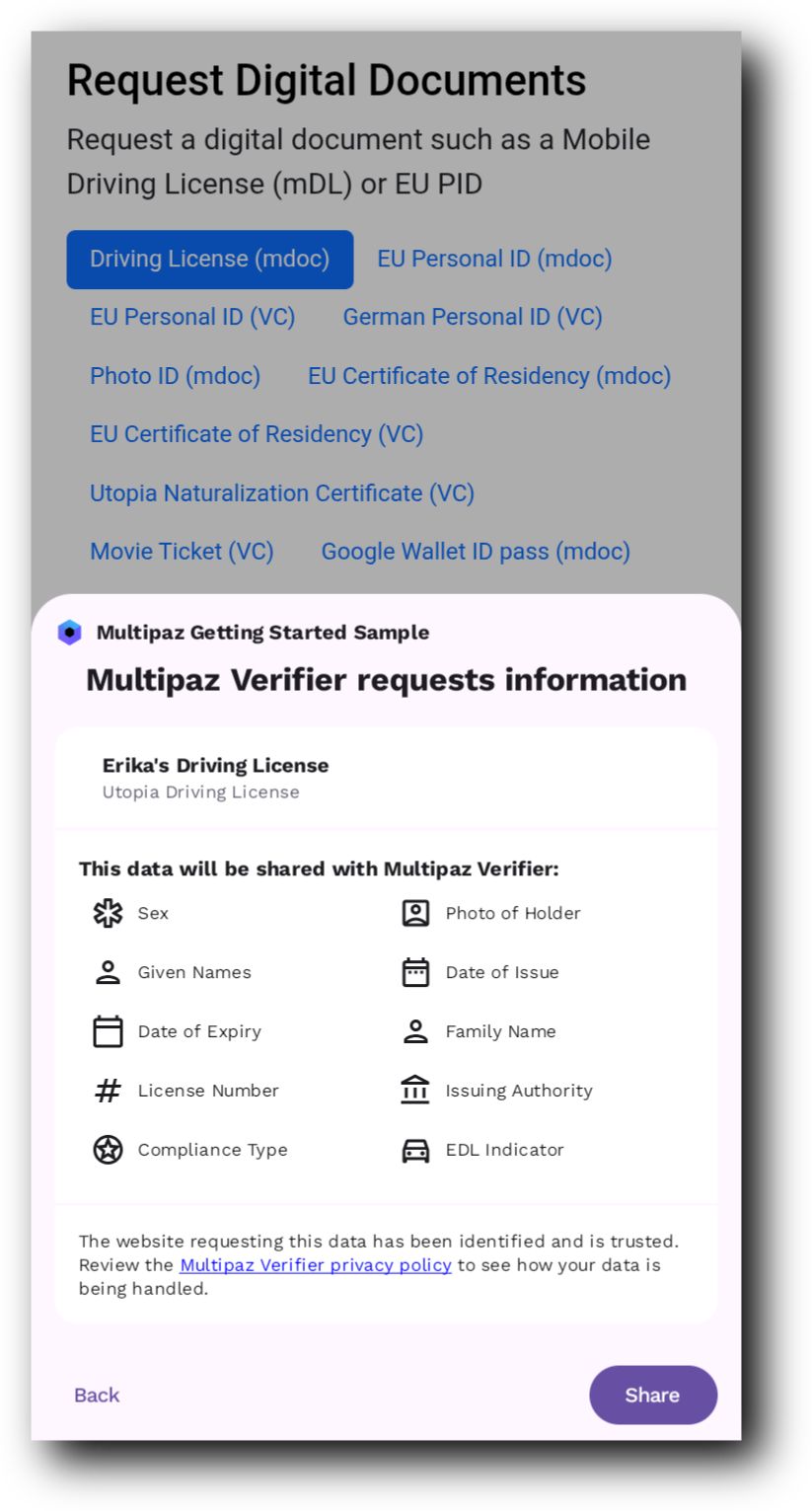
- Follow the on screen instructions & when prompted, select Multipaz Getting Started as the credential provider.
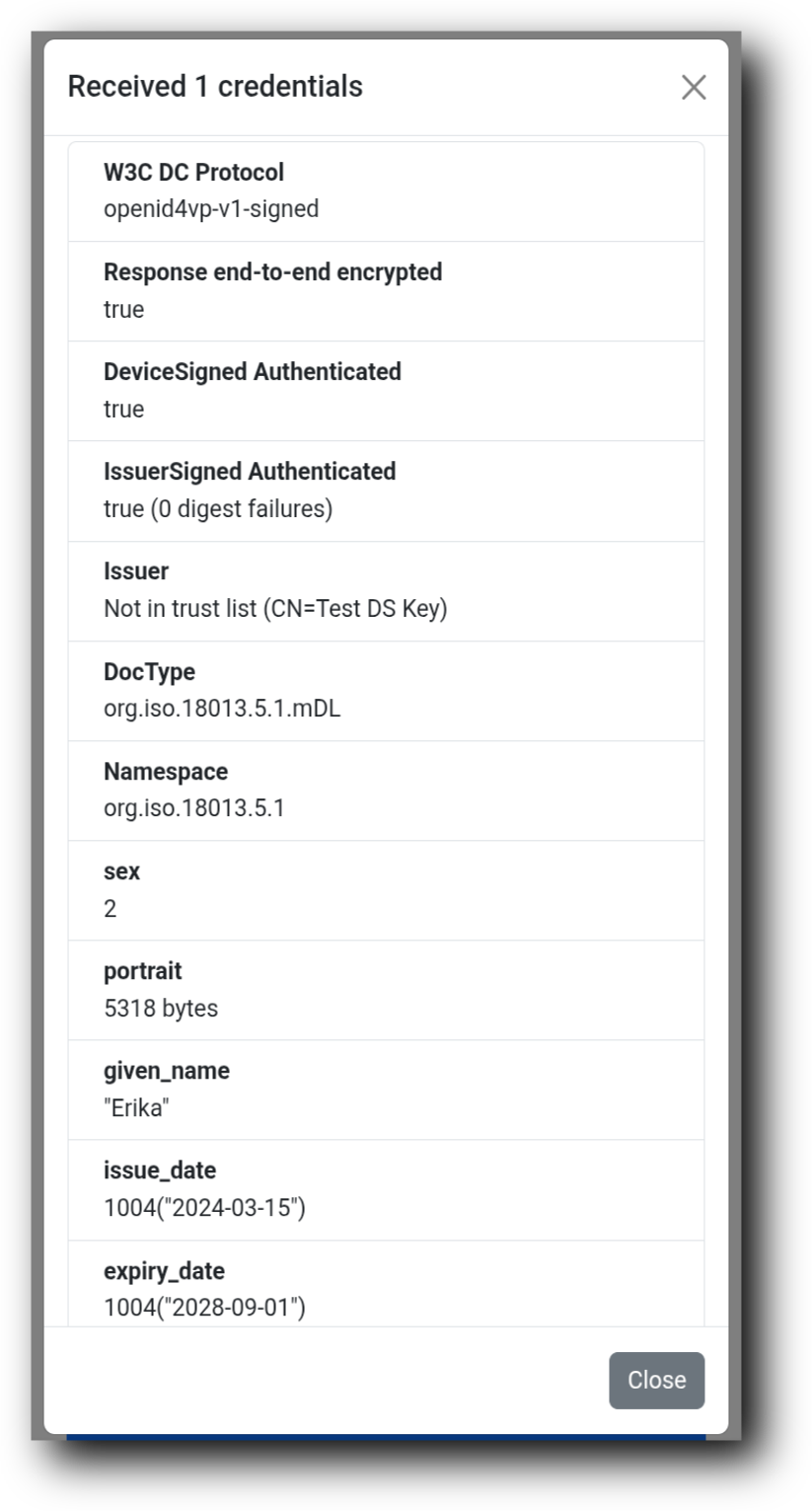
- You will be able to see the details of the received credential in the browser screen.
Demo Screenshots
Security Considerations
- Only browsers listed in
privilegedUserAgents.jsonare trusted when requesting credentials. - The app verifies the calling package and its signature before proceeding.
Server Configuration
The verifier server implementation is available in the Multipaz repository for developers who want to understand the complete flow or build their own verifier:
Repository: multipaz-verifier-server
The server handles:
- W3C DC API endpoint implementation (
/verifier/dcBegin,/verifier/dcGetData) - OpenID4VP (OpenID for Verifiable Presentations) request generation
- Cryptographic verification of returned credentials
- Session management and security validation
This guide only focuses on the credential provider (wallet) side, while the server implementation covers the verifier side of the W3C DC API flow.
By following these steps, your Multipaz Getting Started Sample app will support secure, standards-based credential presentment to web verifiers via the W3C Digital Credentials API.

